What Is an ISP? A Comprehensive Guide to Internet Service Providers
6 min read
15 April 2022
Edvinas Račkauskas
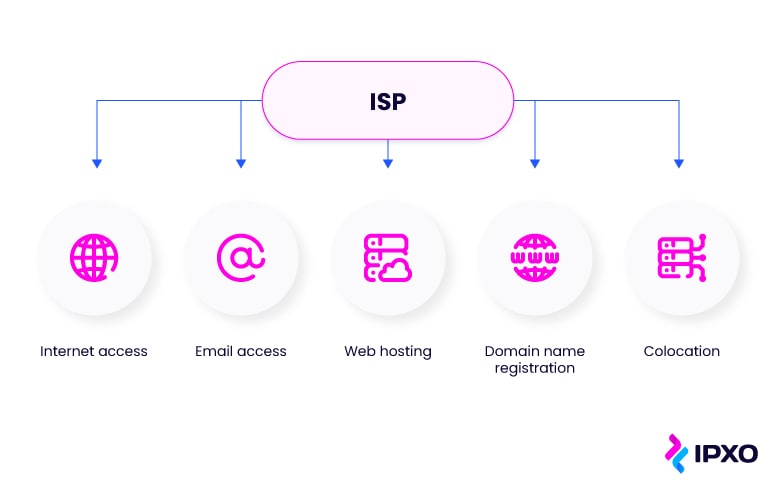
Internet Service Providers play an important role in the world of internet. Learn what ISPs do, what responsibilities they assume and what types of connections they facilitate.
About the author
Edvinas is a Business Analyst at IPXO. Besides providing his insights into the IPv4 market, Edvinas specializes in internet governance, specifically Regional Internet Registries’ policies and regulations. During his free time, Edvinas enjoys exploring new places and travelling to exotic lands.
Table of contents
Related reading
3 December 2021 •
Internet Governance
AFRINIC: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Internet Registry of Africa
Learn more about the African Network Information Centre, where and how it operates, and how it was established.
Read more
29 November 2021 •
Internet Governance
APNIC: All You Need To Know
The Asia Pacific Network Information Centre plays an important role in the management of the internet. Keep reading to learn more about this RIR.
Read more
24 November 2021 •
Internet Governance
LACNIC: All You Need To Know
Internet number resources in Latin America and the Caribbean are allocated by the Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Center – LACNIC. How does this RIR operate and what…
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!