What is a VPN? An Introduction to Virtual Private Networks
How does a Virtual Private Network work? What are the different types of VPN? What are the advantages and disadvantages? Continue reading to learn all about this.

Whether you’re growing a company, streaming your favorite shows or simply trying to keep your data safe online, there’s a good chance you’d benefit from using a virtual private network (VPN) service.
A virtual private network is a service that provides you with a secure and private internet connection wherever you are in the world. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel to keep your data safe, hides your IP address to facilitate anonymous browsing and allows you to remotely access your organization’s network.
VPNs have many applications, from companies scaling their networks to individual users implementing security while connected to public Wi-Fi hotspots.
In this article, we introduce what VPN is and how it works. We also explain some of the more important uses and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of using a VPN.
How does a VPN work?
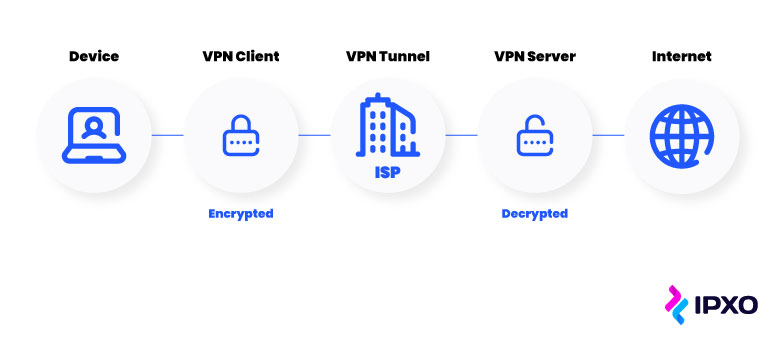
Without a VPN, when you’re browsing the internet, your requests are received by your internet service provider (ISP), who then returns the data you need. For example, by loading a website.
When you use a VPN, things are a little more complicated. Instead of your ISP directing your internet traffic directly to your destination, the traffic first moves through a VPN server.
From your point of view, your public IP address changes to that of the VPN server, and your data is encrypted. However, there’s more going on:
- When connecting to a VPN service, the server authenticates your client.
- An encryption protocol is applied to make all data you send and receive private.
- A secure VPN tunnel is created to transmit data between you and the desired destination.
- Data packets are wrapped in an outer packet by the VPN to ensure a safe transfer.
- The outer packet is decrypted once it arrives at its intended destination.
Types of VPN
While we generally just use the term VPN, there are two different kinds of VPN – remote access and site-to-site access – used on the internet, each with a unique purpose and characteristics.
Remote access
Most of the time, when people refer to VPN, they are talking about a remote access VPN. This kind of VPN is designed to allow users to remotely connect to a computer network securely.
A remote access VPN allows employees to connect to their office network and access files or applications stored in the organization’s servers from anywhere in the world.
For private VPN users, this kind of VPN access generally gives them access to servers operated by their VPN service provider, which allows them to hide their IP address, change their location and browse more securely.
You might also know this version as a virtual private dial-up network (VPDN).
Site-to-site access
A site-to-site VPN is designed for multiple fixed locations to share a single private network.
For example, offices run by the same organization can set up a secure connection over the internet, so that their internal network behaves as if it were one local network. This allows everyone within the organization to access digital resources stored at any location.
This is the less commonly known kind of VPN, especially because it tends to be corporate rather than private. Nevertheless, it is widely used.
VPN encryption explained
One of the biggest appeals of using a VPN is that your data is encrypted and thus safe from the prying eyes of hackers. But how, exactly, does an encrypted VPN connection work?
We briefly mentioned the concept of a VPN tunnel before. While different VPN providers offer different data encryption, the idea of the tunnel and the basics of encryption are relatively universal.
You need to download a VPN app on your computer or mobile device to use the service. This means that the VPN provider has software at both ends of the tunnel – on the server and your device.
When your device requests data, the server fetches the unencrypted data from the internet. However, before relaying it to your device, the server wraps the packet of data in a special layer of encryption.
When the packet reaches your device, the VPN app on your device has the correct key to decrypt the layer of encryption around the packet. Even if the packet was intercepted between the server and your device, without the correct decryption key, it would look like a meaningless string of letters and numbers.
What does VPN secure?
Because VPN protocols create a secure tunnel between the VPN server and your device, a VPN helps keep you secure online in the following ways:
- Encrypts data sent and received by your device, keeping it safe from third parties
- Hides your internet activity from internet service providers, government agencies and hackers
- Hides your IP address, which could be used to compromise your device
- Conceals your real geographical location
- Creates a secure connection on shared or public Wi-Fi networks
Be mindful, however, that even the most reliable VPN provider can’t promise you complete online anonymity and security.

Generally, VPNs aren’t effective against cookies, which companies can use to track your browsing history. And remember, if you’re using a free or cheap VPN, the VPN provider might be collecting data on you themselves.
Moreover, if someone targets you specifically, they could get around your VPN by planting malware on your device or even use traffic patterns from the VPN server to track your traffic.
Undoubtedly, understanding the shortcomings of a VPN can help you figure out which other security steps to take.
Should you use VPN?
A secure connection and private internet access may sound like something you’d want all the time, but VPN protocols aren’t suitable for all users all of the time. Whether you choose to use a VPN depends entirely on your needs.
For instance, if you want to change your IP geolocation, or you’re worried about your personal data privacy on public Wi-Fi networks, using a VPN is a great idea. But you should understand that, as with pretty much every kind of service, there are also some drawbacks to running your internet traffic through a VPN.
To understand whether a VPN service is right for you, you must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of using it.
Advantages of VPN
Before we introduce you to the drawbacks of using your own VPN, let’s explore some of the wonderful and extremely helpful reasons why a virtual private network might be right for you.
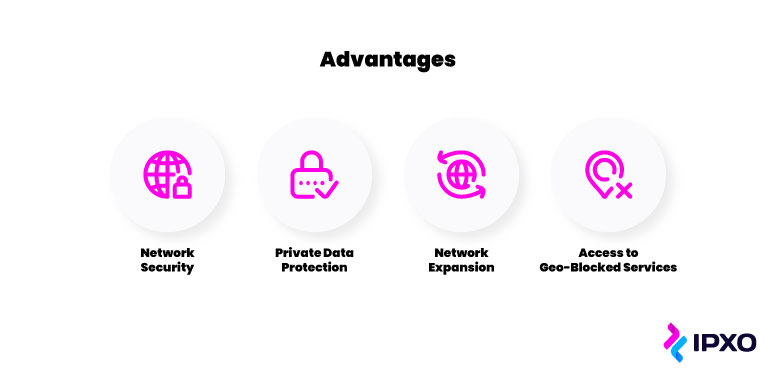
This is not a complete list of advantages; however, these are among the top reasons people use VPN software:
- Network security
- Private data protection
- Network expansion
- Access to geo-blocked services
Network security
Network security is important for everyone, from the most humble social media scroller to huge companies with thousands of connected devices.
For example, websites and web apps tracking your activity while using the internet may pose a risk. At best, your internet data can be harvested by advertisers to personalize ads. At worst, an insecure network could threaten your organization’s security.
To avoid annoying pop-ups or, more importantly, security incidents, you can connect to the internet via a VPN server. Because the VPN encrypts your traffic, you gain a secure connection that, hopefully, no one else can snoop on.
Private data protection
The obvious next question is: why do I need a secure connection? Surely, unless you’re running a company or doing something illegal, there’s no reason to hide your internet connection from everyone else? Unfortunately, we live in a world where hackers are out to gain access to your personal information while you surf the internet.
Think about the online banking, credit card, login credentials and other private details you use online every day. Without an encrypted connection securing your online data, all this personal information is at risk. However, if you use a VPN connection, it hides IP addresses from bad actors and protects all your communication online.
Network expansion
The vast majority of companies and organizations use a private network in their offices and official buildings. This ensures that the network traffic of employees and associates is secure and allows access to specialized virtual workspaces and applications.
However, the problem with running a local network like this is scalability. The cost of growing a network is beyond the budget of many organizations. A virtual private network can save the day. Using a corporate VPN server allows anyone with the correct credentials to access the network remotely, provided they have an internet connection.
This kind of remote access VPN keeps all traffic on the same secure network and provides an encrypted tunnel for employees to access applications not available on their own machines. This could be anything from company emails to payroll systems that need to be handled with the utmost sensitivity.
Access to geo-blocked services
Have you ever gone on holiday only to discover your favorite show is no longer on Netflix? Or perhaps you happen to know that flight tickets are cheaper if you buy them from a different country?
While the internet feels free and global, online services use your IP address to determine where you are in the world geographically. They then use that information to show or hide geo-specific content or services.
You’ve probably guessed by now that this is another way in which VPN servers can come in handy. Your VPN connection can use an IP address associated with an entirely different location, so you can choose where in the world you want to be seen accessing the internet from.
This leaves you free to access all the content and services you need.
Disadvantages of VPN
A VPN protects your data, encrypts your connection and gives you access to more content and services. It’s a win-win situation, right? Well, unfortunately, it’s not.
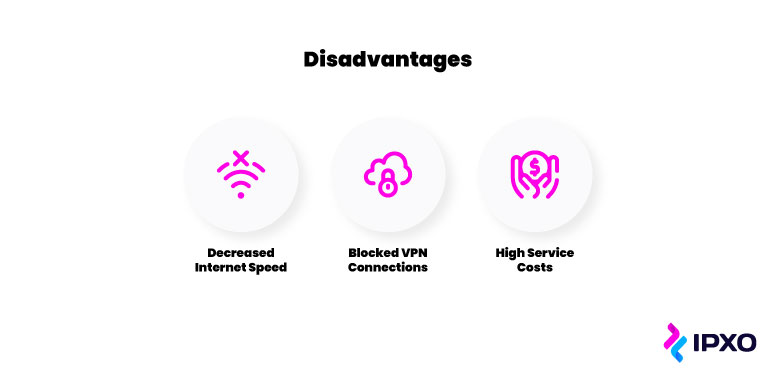
As with all things in life, there are some drawbacks to using VPNs online. Here are some of the most compelling reasons not to use a VPN connection all the time:
- Decreased internet speed
- Blocked VPN connections
- High costs
VPN disadvantages
Decreased internet speed
The elephant in the room is that using a VPN service has speed issues associated with it. Because a VPN works by rerouting and encrypting your internet connection, it can slow it down.
That said, for the average user with average internet traffic, VPN-related connection slowdowns will be negligible. In most cases, users might not even notice it. Moreover, premium VPN services slow traffic down minimally.
However, suppose you’re streaming, gaming or doing some other kind of bandwidth-intensive activity online. In that case, you may find that your VPN restricts speeds to the point where it can become inconvenient and annoying.
This is the biggest complaint that many VPN providers receive from their customers.
Blocked VPN connections
A good VPN offers freedom and security; however, not every service provider is a fan.
For example, take big streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu or HBO. VPN users utilize their VPN client software to access geo-blocked content on these platforms, and the companies know it.
Streaming platforms are incentivized to block VPN internet traffic to protect their licensing and intellectual property. While the best premium VPNs will usually allow you to access these services from another location, the majority of cheap and free ones are now blocked.
VPNs also disable ISP tracking, which stops your internet service provider from collecting data about your online activities. That said, your internet provider can see when you’re using a VPN.
And it’s not just private companies that are unhappy with VPN providers. Believe it or not, some countries have made using VPN illegal, while others have taken steps to restrict the use.
This kind of internet censorship isn’t an issue unless you plan to use a VPN client somewhere like Belarus, China or Iraq. However, it’s worth remembering that the online identity protection and security offered by the technology are not available to all.
Cost
Premium VPN services are premium because they can cost a fair amount of money. You can get a decent VPN for personal use for a few dollars per month, but if you’re running a business, a VPN subscription for all your employees can start to run up to a significant amount of money.
Naturally, the more you’re willing to spend on VPN services, the better, more dependable, faster and more secure they are going to be. Sure, free VPNs exist, but you need to ask yourself why anyone would give you anything for free. Perhaps, the free VPN service you’ve chosen either doesn’t work or poses a security risk?
Due to data collection, advertisements and download restrictions, you might find that using cheap or free VPNs is worse than not using them at all.
Conclusion
A VPN allows a user to connect securely to a remote computer network. Most commonly, it is used by companies to enable employees to access company servers remotely. Individual internet users often use VPNs to increase their security while using the internet or to bypass restrictions.
A VPN encrypts data that your computer sends and receives, and it also hides your IP address. This can help you browse privately, enhance the security of your personal data and enable you to access services and content not available in your physical location.
Although VPNs have some downsides – most notably, the decreased traffic speeds – using a VPN is advantageous in many ways and can offer security that outweighs any drawbacks.
About the author
Table of contents
How does a VPN work?
Types of VPN
Remote access
Site-to-site access
VPN encryption explained
What does VPN secure?
Should you use VPN?
Advantages of VPN
Network security
Private data protection
Network expansion
Access to geo-blocked services
Disadvantages of VPN
Decreased internet speed
Blocked VPN connections
Cost
Conclusion
Related reading

DNS and rDNS: the Hidden Heroes That Keep the Internet Running
Discover the web's overlooked helpers - DNS & rDNS. Learn their importance, benefits, and automation's role in powering the online world.
Read more
Email Service Provider: What You Should Know About ESPs in 2022
Discover the differences between email service providers and webmail clients. Learn the importance of ESPs for successful email marketing campaigns.
Read more
File Transfer Protocol Explained
What does FTP stand for? What is the importance of this protocol? How does it work? Read this post to learn all about the File Transfer Protocol.
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!
