WAN vs. LAN: Comparing Wide Area Network to Local Area Network
6 min read
21 January 2022
Mindaugas Kubilius
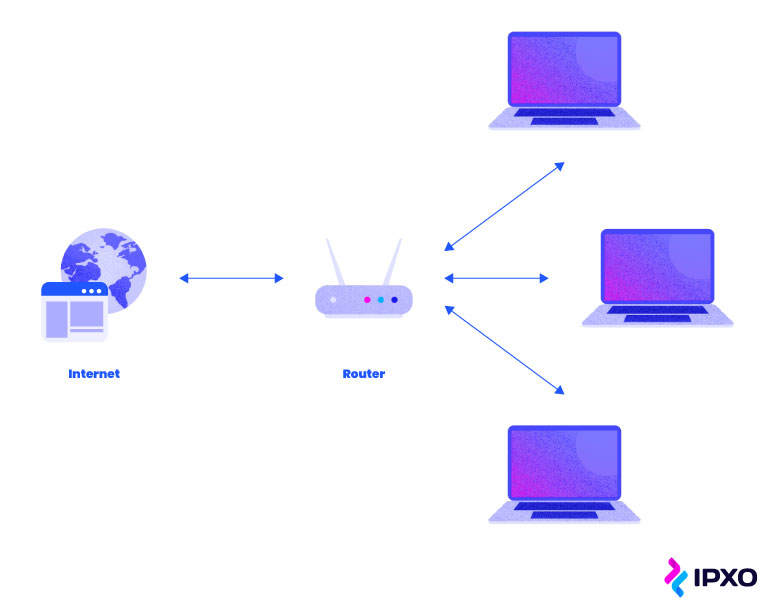
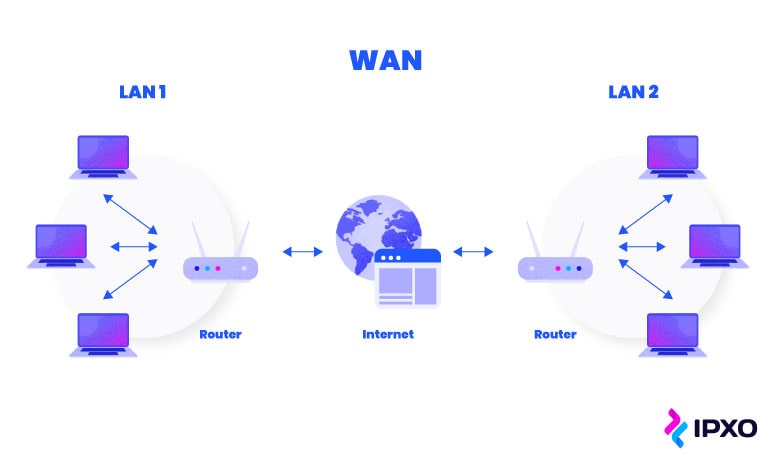
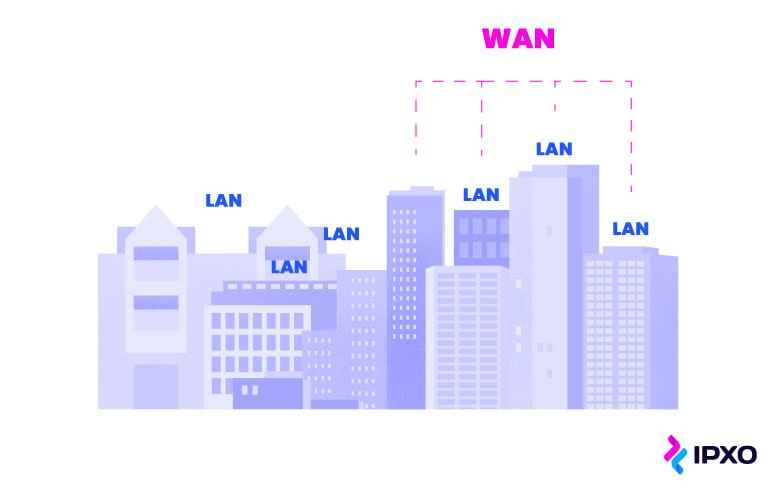
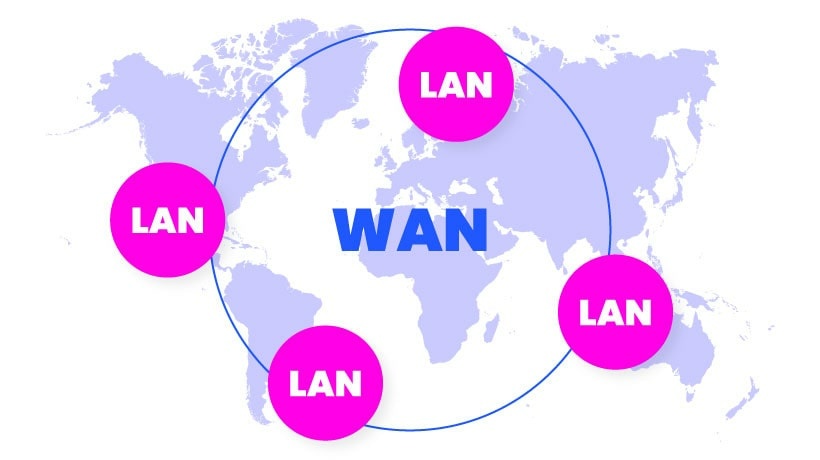
What is a local area network? What is a wide area network? How do they differ and how are they similar? You can find answers to these questions in this post.
About the author
Mindaugas is a Network Administrator at IPXO with more than 15 years of experience in the IT field. He specializes in building and maintaining various network infrastructures, as well as presenting top-notch engineering solutions to the public. After work, Mindaugas spends his time in nature.
Table of contents
Related reading

6 September 2023 •
Network Engineering
DNS and rDNS: the Hidden Heroes That Keep the Internet Running
Discover the web's overlooked helpers - DNS & rDNS. Learn their importance, benefits, and automation's role in powering the online world.
Read more
19 July 2022 •
Network Engineering
Email Service Provider: What You Should Know About ESPs in 2022
Discover the differences between email service providers and webmail clients. Learn the importance of ESPs for successful email marketing campaigns.
Read more
12 July 2022 •
Network Engineering,
Networking Protocols
File Transfer Protocol Explained
What does FTP stand for? What is the importance of this protocol? How does it work? Read this post to learn all about the File Transfer Protocol.
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!