Knowledge Base » Technical Guides » IP Geolocation Guide
IP Geolocation Guide
Learn what IP geolocation is and what to do if you want to change it.
What is IP geolocation and what is it for?
An IP address is a unique identifier of a device on the Internet. IP geolocation is the data that represents the geographical location of that device. When you have IP geolocation data, you can determine such physical location information as the country, area and city as well as the ISP.
IP geolocation databases are commonly used to determine users’ locations to present them with more personalized promotional content.
Example
For this example, we use iplocation.net to perform IP Lookup on 185.141.165.74.
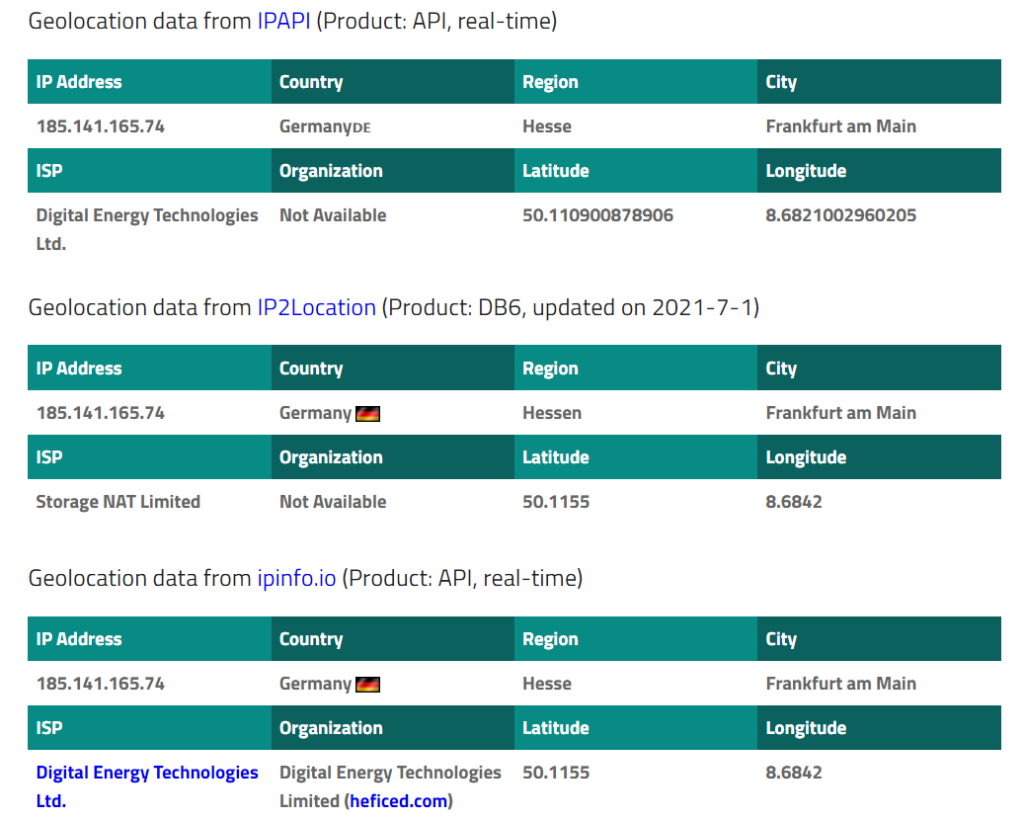
The IP Lookup tool found the IP record on IPAPI, IP2Location and IPinfo.io databases. The information provided in the brackets next to the source name reveals where the data comes from and when it was updated.
How to find traceroutes
Database supervisors might ask traceroutes to your IP to confirm accurate IP geolocation data. Windows OS users can use the Command Prompt to provide this information.
Enter cmd into Windows search to find Command Prompt and click it to open.
Enter the following command (instead of your_ip, enter the IP you want to trace):
tracert your_ip
Let’s use 185.141.165.74 as an example once again.
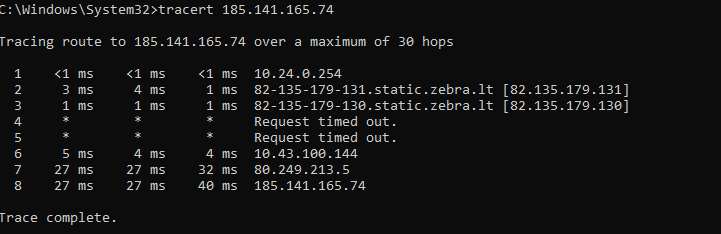
Note: The traceroute data depends on the location it is performed in. The tool checks connections from one PoP to another, mapping the route.
In the Command Prompt, the first column shows the number of a hop. The second, third and fourth columns show the latency between the hops. The fifth column shows the address of the hop. The * symbol presents hidden latency information between PoPs due to security reasons.
If you have to produce a traceroute, copy the results presented by cmd to a text file. Send this file to the database supervisor, who requested the traceroute information.
To learn how to change your geolocation, please refer to our IPXO Geofeed Guide.
Contact Customer Solutions
If you have any questions, contact our Customer Solutions Team