The Evolution of Route Origin Authorization: Insights from IPXO’s Half-Year Journey
Discover the transformative power of Route Origin Authorization and fortify your network's security and efficiency with valuable insights from IPXO's mid-2023 journey.

In today’s rapidly progressing digital domain, ensuring a secure and efficient network infrastructure is paramount. One powerful tool that has gained prominence is Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) and its key component, Route Origin Authorization (ROA).
IPXO, a leader in the field, has embraced ROA for the past six months, gaining valuable insights and experiencing the benefits it brings to the internet ecosystem. In this blog post, we will delve into IPXO’s journey with ROA, explore its features and interactions with Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), demonstrate its tangible benefits, and analyze its global adoption and impact on network security practices.
Key takeaways:
- Route Origin Authorization (ROA) is a powerful tool for enhancing routing security and fortifying network infrastructure in the digital domain.
- IPXO, the next-gen IPAM platform, has embraced ROA for six months, gaining valuable insights and experiencing its benefits for internet ecosystem security.
- Global ROA implementation, which now makes up 34%, has significantly improved network security practices, preventing route hijacking, enhancing routing security, and increasing network resilience.
The meaning of Route Origin Authorization
ROA is a cryptographically signed object that states which Autonomous System (AS) is authorized to originate a certain prefix – a portion of the IP address space. It is a method for verifying that the specific prefix or IP address holder has authorized an AS to originate route objects in the inter-domain routing environment for that prefix.
ROAs are composed of the following elements:
- Prefix: Specifies the range of IP addresses that the ROA is authorizing, expressed in CIDR notation
- Maximum Length: Indicates the longest prefix length (in bits) for which the ROA is valid, allowing more specific or less specific prefixes within the range
- AS Number: The Autonomous System Number (ASN) identifies the Autonomous System (AS) that can originate the specified prefix
- Signature: The ROA is cryptographically signed using a private key to validate its authenticity and integrity
ROA is part of the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) system, which was proposed in 2005 by Geoff Huston and Randy Bush to improve routing security in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and the Internet’s global routing system. Subsequently, RPKI underwent several years of development and standardization, with the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) publishing initial standards in 2010.
Since then, ROA has been gradually adopted by network operators and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to reinforce the security and trustworthiness of route announcements.
All your IP-related needs in one place
Try IPXO now and experience seamless IP solutions!
ROA evolution: Insights from IPXO
Over the past six months, IPXO has extensively explored the world of ROA, gaining valuable insights and experiences through collaboration with RIRs. This collaboration has provided IPXO with a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies and benefits of ROA implementation.
As IPXO began delegating RPKI, the number of delegations to the company steadily increased, resulting in a significant expansion of ROA within IPXO. The company consistently and promptly created and revoked RPKI (ROA) based on authorized announcements.
As shown in the graph below, the global number of Route Origin Authorizations has significantly risen from the beginning of the year 2023, increasing from 391,031 to 442,051, highlighting the continuous growth and widespread impact of ROA implementation.
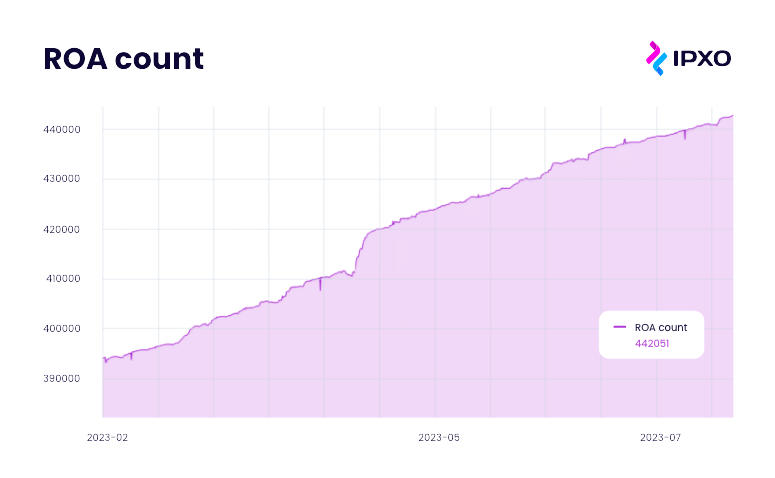
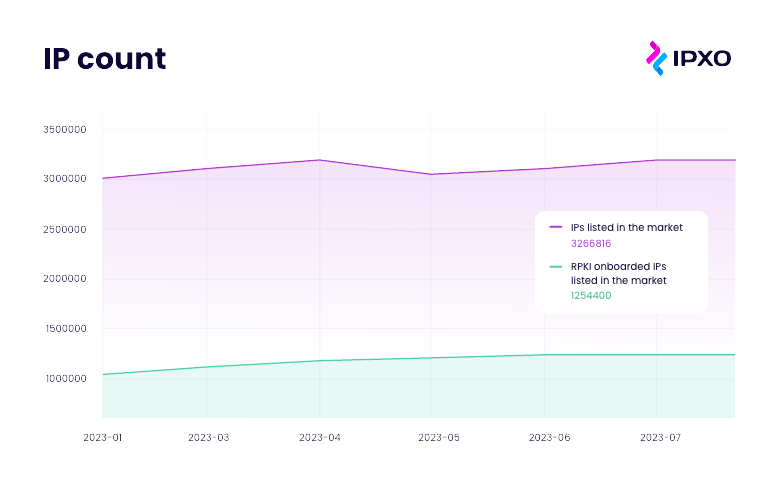
Currently, out of 3.2 million subnets in IPXO Marketplace, Delegated RPKI encompasses 38.4% of them. This demonstrates the substantial influence of Route Origin Authorization implementation and its positive effects on IPXO’s network management and security.
Additionally, it also allows clients to activate their leased subnets quickly, as they receive immediate authorization as soon as an ASN is assigned to them. This streamlined process ensures a smoother experience for clients and further enhances the efficiency of IPXO’s services.
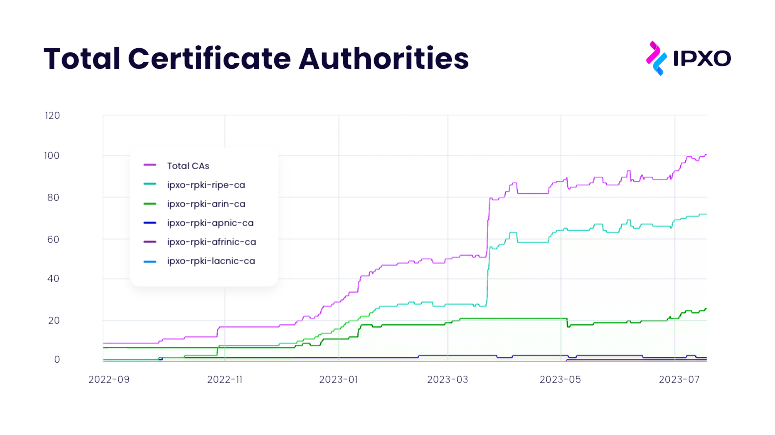
In the provided screenshot, you can observe that the delegated Regional Internet Registries are primarily RIPE NCC and ARIN, which are widely popular, and offer the Delegated RPKI Management option. On the other hand, some other RIRs, such as AFRINIC, offer only the standard Hosted RPKI option.
IPXO provides its customers with the flexibility to choose the ROA prefix Maximum Length size, emphasizing the importance of making educated decisions and issuing ROAs based on exact needs, aligning with Manually Agreed Norms for Routing Security (MANRS) ideology and recommendations. The latter advocate issuing ROAs based on exact needs rather than using a single large ROA to cover multiple smaller announcements.
Demonstrating the benefits of Route Origin Authorization
Therefore, ROA is a powerful mechanism that significantly contributes to a more secure and efficient network. Drawing from recent experiences, IPXO has witnessed firsthand how Route Origin Authorization enhances network security and performance, leading to several notable benefits:
a) Secure internet routing
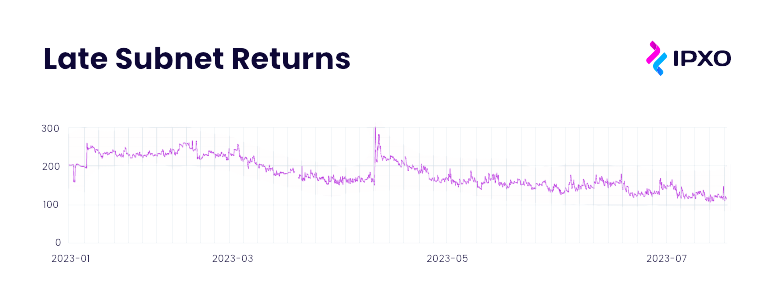
With ROA, IPXO can authorize the origin of their IP address prefixes, effectively ensuring subnets are promptly returned to the marketplace upon lease termination. The screenshot below shows the number of subnets in the IPXO Marketplace that were still being announced by former clients after their leases ended.
However, the graph clearly indicates a positive trend over the last six months, with a decrease in late subnet returns. This improvement can be attributed to the increased implementation of RPKI and RPKI Delegation at IPXO, which has enabled automated and expedient handling of ROA revocation when leases conclude. This facilitates the timely return of subnets to the marketplace for new leasing.
Moreover, with each new delegation, IPXO gains better control over the numbers and supplements it with its quarantine system. This system ensures that after revocation, subnets are not immediately reintroduced to the Marketplace until all announcements are fully sorted out.
To address this, IPXO has an automatic email mechanism that requests assistance from IP holders and clients to resolve any lingering announcements, resulting in a crucial role played by the quarantine system in decreasing the workload for our Abuse and Support teams.
b) Improved efficiency
Furthermore, ROA enables IPXO to streamline its routing policies through origin validation of announced routes, leading to reduced routing table size, faster convergence, and overall improved network efficiency. The substantial impact of this implementation is demonstrated by the two graphs below, which reveal a significant trend in the successful parking of previously unleased subnets.
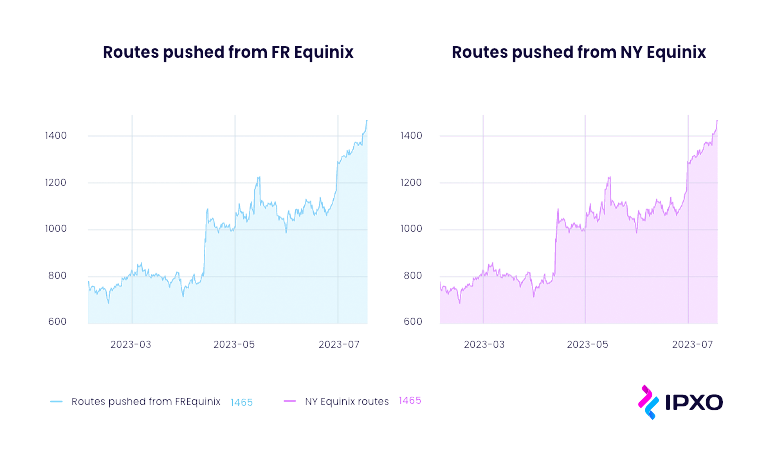
Parking involves reserving or holding IP address space for future use, primarily to protect the subnet from potential hijacks after it has been leased. Some individuals actively search for unused IP addresses and may use or announce them illegally.
By implementing parking and having a valid ROA in place, IPXO disrupts this hijacking process and may even prevent it entirely by revoking the hijacker’s authorization through the ROA. This practice of parking enhances IPXO’s network security and contributes to a more robust and reliable routing infrastructure.
The substantial impact can be attributed to two key factors:
- Implementation of Automation. Automation allows for faster identification and revocation of non-authorized announcements within the network, ensuring prompt removal of unauthorized routes. This directly aligns with the improved network efficiency, as unauthorized announcements can be promptly detected and addressed, reducing unnecessary routing table entries.
- Delegation of ROA to IPXO with AS834. The delegation of authorization to IPXO plays a crucial role in enabling ISPs to effectively announce and park subnets online until they are leased again. This efficient authorization process contributes to improved network efficiency and management, reducing the number of unauthorized or improperly announced routes and promoting overall network stability.
Overall, the combination of ROA implementation, parking practices, and automation at IPXO has resulted in notable improvements in network efficiency and security.
Ready to revolutionize your network security and efficiency?
Join IPXO on a journey to a safer, more efficient internet!
Analyzing global adoption of ROA
ROA’s impact extends beyond IPXO’s own experiences, influencing network security practices worldwide. Moreover, based on MANRS Community Report 2022, the global adoption of ROAs is 34%, reflecting the collective commitment of internet service providers worldwide to embrace ROAs in order to enhance routing security and fortify their networks.
Furthermore, according to Cloudflare statistics, as of July 2023, there have been 449,808 ROAs in the global Resource Public Key Infrastructure system, and the numbers are steadily growing. This widespread adoption of ROA has improved network security practices globally in several ways:
Preventing route hijacking
ROAs help prevent route hijacking, a type of attack in which an attacker takes control of a legitimate IP address block by announcing it from a different AS. This can be done by exploiting vulnerabilities in the BGP, which is used to exchange routing information between Autonomous Systems. By using ROAs, network operators can verify that a BGP announcement is legitimate and authorized by the address holder, preventing unauthorized announcements from being propagated worldwide.
Improving routing security
ROAs are a critical step forward in securing the global BGP system to prevent mis-originations and errors from propagating invalid routing information globally. By validating BGP route announcements, ROAs enable network operators to classify BGP announcements as valid, invalid, or not found, thus improving routing security.
Enhancing network resilience
Additionally, ROAs can enhance network resilience by providing a mechanism for detecting and mitigating routing anomalies, such as route leaks and hijacks. By filtering unauthorized BGP announcements, network operators can prevent malicious routing information from being propagated, thus improving the overall resilience of the network.
Streamlining ROA creation and maintenance
Furthermore, several organizations, such as ARIN, have introduced streamlined processes for ROA creation and maintenance, making it easier for network operators to implement ROAs. This has helped increase the adoption of ROAs and improve network security practices globally.
Overall, ROAs have significantly impacted network security practices worldwide, addressing issues like route hijacking and improving comprehensive routing security and network resilience. The streamlined processes introduced by organizations like ARIN have facilitated easier ROA implementation, contributing to the security and reliability of the Internet.
This collective effort by network operators, supported by the prevalence of ROA adoption, is paving the way for a more secure and resilient global routing infrastructure.
Conclusion
Route Origin Authorization has emerged as a crucial component in fortifying the security and efficiency of internet networks. IPXO’s half-year journey with ROA has provided valuable insights and firsthand experiences, showcasing the benefits it brings to the internet ecosystem.
Through enhanced routing security, improved efficiency, and its global impact on network security practices, ROA has proven to be a powerful tool for ensuring a more secure and reliable internet infrastructure.
Consequently, as IPXO continues to harness the potential of ROA, we eagerly anticipate further advancements in network security and the broader adoption of this critical technology.
FAQs about Route Origin Authorization
ROA verification involves cryptographically signed objects that include the prefix, maximum length, AS number, and a signature. These elements validate that the AS is authorized to originate the specified prefix, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the route announcement.
Global ROA adoption is crucial for improving overall internet routing security. By encouraging network operators worldwide to adopt ROAs, we can collectively prevent malicious route hijacking and improve the resilience of the internet’s routing infrastructure.
For ISPs, ROA implementation enhances routing security by providing a mechanism to verify authorized route announcements. It reduces the risk of routing anomalies, improves network efficiency, and fosters a culture of trust and accountability among network operators.
Alignment with MANRS ideology and recommendations provides a standardized and secure approach to ROA management. Implementing MANRS guidelines ensures that ROAs are accurately validated and renewed, reducing the risk of network disruptions due to incorrect or invalid ROAs. With clear responsibilities for ROA maintenance and auto-renewal options, network operators can efficiently manage their ROAs without manual intervention.
ROA has significantly impacted network security practices worldwide by addressing issues like route hijacking, improving comprehensive routing security, and enhancing network resilience. This collective effort by network operators, supported by the prevalence of ROA adoption, paves the way for a more secure and resilient global routing infrastructure.
About the author
Table of contents
Key takeaways:
The meaning of Route Origin Authorization
ROA evolution: Insights from IPXO
Demonstrating the benefits of Route Origin Authorization
a) Secure internet routing
b) Improved efficiency
Analyzing global adoption of ROA
Preventing route hijacking
Improving routing security
Enhancing network resilience
Streamlining ROA creation and maintenance
Conclusion
FAQs about Route Origin Authorization
Related reading

Open Internet and IP Address Management
Embrace the Open Internet's principles and navigate the evolving landscape of IP address management. Discover how we're adapting to new realities at IPXO, empowering you with access to IP…
Read more
What Is More Energy-Efficient: IPv4 or IPv6?
The transition to IPv6 holds the potential to reduce global energy consumption and foster a sustainable future in networking. However, the slow adoption rates of IPv6 have prompted alternative…
Read more
First Came IPv4, Then IPv6. What Happened to IPv5?
IPv4 and IPv6 are the only two versions of the Internet Protocol in use. Discover what happened to IPv5 and whether or not the current versions of the Internet…
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!
