SSL vs. TLS: A Beginner’s Guide to Security Protocols
6 min read
28 April 2022
Beatričė Raščiūtė
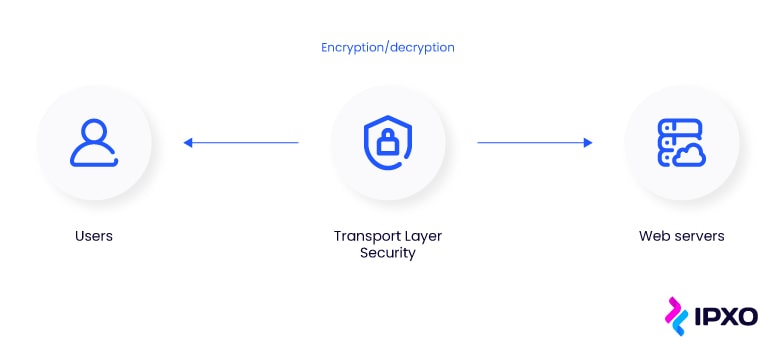
Discover the differences between SSL and TLS, as well as their working mechanisms.

About the author
Beatričė is a Technical Content Writer at IPXO. Having experience in translations, she decided to test new waters in the tech industry as a writer. While creating content, she dives deep into different internet and networking topics with the goal to present valuable information in the most reader-friendly way.
Table of contents
Related reading

2 August 2022 •
Internet Protocol,
Networking Protocols
IPv4 Packet Header: Format and Structure
When you think about it, the IPv4 packet format is truly fascinating. Learn about the elements at play with this comprehensive guide.
Read more
12 July 2022 •
Network Engineering,
Networking Protocols
File Transfer Protocol Explained
What does FTP stand for? What is the importance of this protocol? How does it work? Read this post to learn all about the File Transfer Protocol.
Read more
7 June 2022 •
Internet Protocol,
Networking Protocols
TCP/IP: What Is It And How Does It Work?
The Transmission Control Protocol and the Internet Protocol create what is known a TCP/IP model. Learn how it works and what functions it serves.
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!