VPN vs. Proxy: Key Differences
To compare VPN vs. proxy and choose between the two, it is essential to understand how both services work and what each has to offer.

In 2021, 31% of global internet users used a virtual private network (VPN) for a more anonymous access to the internet. However, a VPN is not the only service offering higher online anonymity. A proxy is another option to consider. The question is: Can internet users use these services interchangeably? We compare VPN vs. proxy in this article to get down to the bottom.
A proxy and VPN act as intermediary servers between the user and the internet. Since both a VPN and a proxy server can make the user’s traffic appear to come from a remote IP address, it may look like they offer the same service, but they are different. While VPN connections provide more data security and privacy, most proxy server connections do not.
So, how do a VPN and a proxy server work and what are the key differences between the two? Keep reading to learn more.
What is a VPN server?
A virtual private network is a service that offers a more secure online connection. A VPN encrypts the users’ internet traffic from their device to the VPN server and hides their IP address by redirecting the traffic through a remote server. This means that an internet service provider (ISP) and third parties, like governmental organizations or advertisers, have a harder time monitoring what websites users visit or what data they transfer and receive.
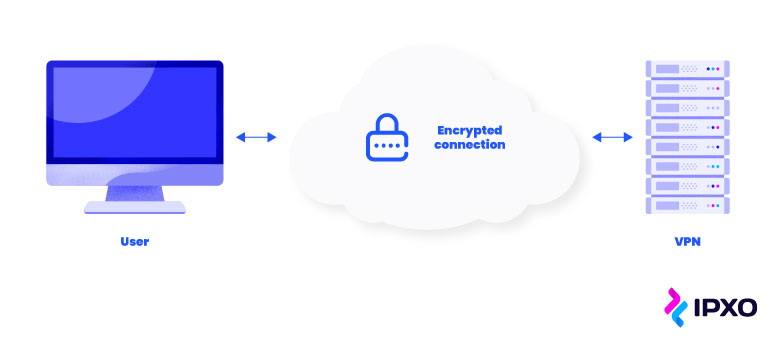
Basically, if governments or ISPs were to track a user’s location or online activity, it would be related to the remote IP address of a VPN server, not a particular person. Moreover, VPN service providers can have many VPN servers in different locations, and the user’s activity may be related to any of them.
Types of VPN
Usually, a virtual private network is called a VPN, but there are two types:
- Remote access VPN
- Site-to-site-access VPN
A remote access VPN is more suitable for personal use, while a site-to-site access VPN is better for businesses and large organizations.
A remote access VPN connects the user to a safe remote server so that they can use private networks and resources. For example, it enables remote employees to safely access corporate networks as if they were working from the office.
Larger organizations, on the other hand, usually use site-to-site VPN services. Companies that have many offices in different locations frequently use a site-to-site VPN to ensure a safe connection between different departments. This way, all employees from different offices can access the company’s resources.
Moreover, if large-scale businesses have many employees, store and manage a lot of sensitive data, the implementation of VPN services may require more resources to ensure secure access. For example, if a company uses more than one VPN to provide access to different remote employees, the IT team might need to set up different VPN clients on employees’ computers and keep the software up to date.
What is a proxy server?
To put it simply, a proxy server is a machine that sits between the user and the final server and helps access websites indirectly. Basically, when a user connects to the website or another application, they first connect to the proxy. After that, a proxy connects the user to the website via an outside host server.
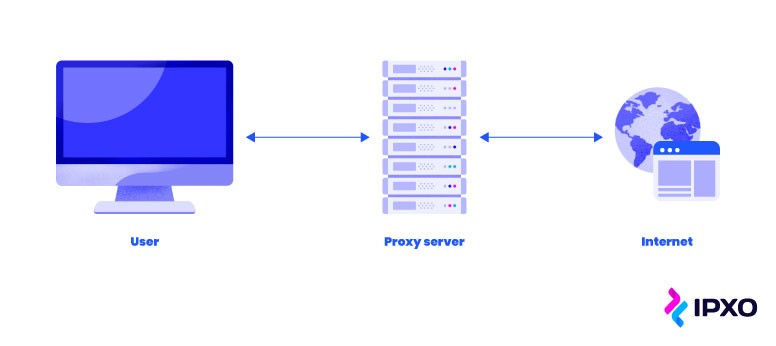
This function has a clear benefit: The proxy server hides the user’s original IP address, and the website sees the IP address of the proxy server. This is ideal if users want to browse the internet anonymously or access geo-restricted content. The latter can be inaccessible due to your real geographical location. Hiding the true location can unlock the restricted content.
However, some streaming services may have proxy blocks that proxy servers cannot get around. For example, Netflix introduces that using the so-called Netflix proxy error message.
Most importantly, not all proxy servers encrypt internet traffic. Unfortunately, wrongdoers (e.g., cybercriminals) might infiltrate the network and steal users’ private information. This means that users using proxies might end up with a less secure connection to the internet and, consequently, put their data and identity at risk.
Types of proxy server protocols
Different types of proxy server protocols define how proxy servers are configured. We are going to discuss four of them briefly:
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Socket Secure Protocol (SOCKS)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Transport Layer Security Protocol (TLS)
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) proxies are the most popular type of proxies that help access web pages. With the help of HTTP proxies, the web traffic is carried through the HTTP proxy server.
By concealing a user’s IP address, an HTTP proxy can help access geo-restricted content. For example, Youtube videos that are not available in a specific region. Moreover, HTTP proxies can cache frequent or recent web page requests to increase the website load speed.
SOCKS
Another type of protocol is known as Socket Secure (SOCKS), and the latest version, SOCKS5, is considered the most advanced version of the protocol. Unlike HTTP proxies, SOCKS can handle any program or web traffic. For example, by setting up SOCKS, users can access their chosen video streaming app or even online games that might not be available due to their geographical location.
Compared to an HTTP proxy, SOCKS supports several types of authentication, which means enhanced security. That’s because if users want to connect to the proxy, they need to provide a username and password.
Furthermore, SOCKS may be a great option for those who need to efficiently download or transfer large amounts of data through the internet. On the other hand, these proxy servers may be slower due to higher popularity and bigger load.
FTP
The third proxy server protocol is the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Users can use it to transfer files, such as photos or documents, between computers. Websites employ FTP to upload and download files too. Even though the FTP protocol alone does not offer encryption and security of uploaded files, it may help protect them.
TLS
Lastly, we have the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, which replaced the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). This cryptographic protocol ensures that data sent over the internet is encrypted. By encrypting the traffic, TLS ensures secure transmission of the users’ data from the client to the server and provides a higher level of anonymity.
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) combines TLS/SSL with HTTP to introduce a more secure HTTP version.

Comparing VPN vs. proxy
While both VPN and proxy hide your IP address, these two services differ in how they handle users’ traffic and data. They also differ in pricing. The biggest differences between a VPN and a proxy can be observed in regards to:
- Security
- Encryption
- Speed
- Pricing
Security
Both proxy and VPN connect to a remote server before they connect to a website or application. This means that both act as the middlemen between the user and the website or web app, and both hide users’ IPs to facilitate anonymous browsing.
Proxy security
While proxy servers can handle only web requests, virtual private networks can hide all network traffic. In other words, VPNs work on the operating system level, and proxies operate only on the application level. Therefore, if users want to hide all traffic from their internet service providers or other organizations, a VPN might be the more suitable option.
Furthermore, depending on the proxy server, an ISP can see that users are connected to it and what sites or services they visit, not to mention the data users might receive or send as well.
If that is not enough, the proxy server owner can peek at the information going through the proxy server. Since a proxy provider might see the user’s sensitive data, like login credentials, the trustworthiness of this provider must be considered carefully.
By gaining access to sensitive data, such as usernames and passwords, an unreliable proxy owner might sell it to make money. It is also possible that cybercriminals can abuse proxy servers to perform malicious activities.
You should be especially careful about free proxy servers since many block the HTTPS protocol and may snoop on users’ private data, like credit card numbers.
VPN security
Different VPN providers have different data policies too. For example, some can log users’ IP addresses or websites they visit. Other VPN providers do not log any data (no-log VPNs), meaning they do not track their users’ traffic.
Furthermore, different VPN providers can offer different built-in security features that block malicious websites, for example, malware website blocking or anti-phishing protection. In combination with reliable anti-virus software, these features can help prevent malware from entering users’ devices. This, in turn, can help evade scams and cyberattacks, thereby enhancing data security.
Similarly, proxies can also complement anti-virus software with firewalls and protect users’ data at some level. However, note that both proxy and VPN only offer additional preventative measures. Users should still beware of spam emails sending malicious attachments or websites promoting dangerous download links that might threaten their security.
Encryption
While not all proxies provide encryption capabilities, premium VPNs offer a more secure connection by rerouting traffic through an encrypted tunnel. Only a VPN can do that. However, the traffic from the VPN server going to the web server may be unencrypted, which means that a VPN does not provide end-to-end encryption. Still, a VPN effectively ensures higher online security.
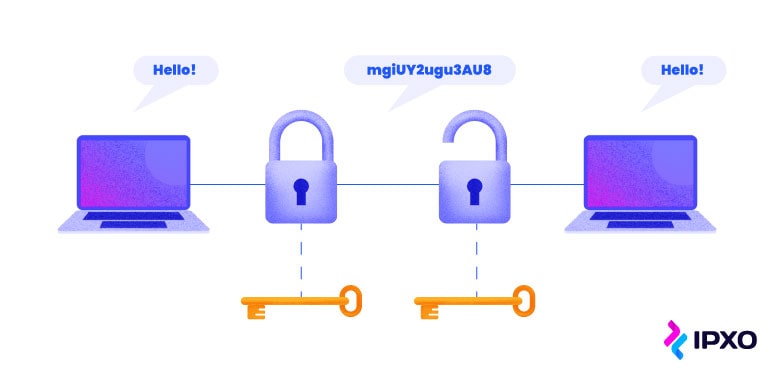
For example, using a VPN, users can access their banking services more safely, especially if they need to use a public Wi-Fi network. Luckily, hackers would have a hard time stealing VPN-encrypted data like credit card numbers. Even if they managed to reach sensitive data, it would be difficult to decipher it without a decryption key.
Moreover, a VPN service can prevent ISPs from tracking their users. With a VPN turned on, ISPs can only see that their users are connected to a VPN. To further increase privacy, no-log VPNs ensure that information about users’ internet activity is protected even if the government or other organization asks for it.
In comparison, not every proxy connection offers encryption; therefore, ISPs and other third parties can see unencrypted traffic. Even though some proxies, like SOCKS, provide authentication solutions, they are still vulnerable to data breaches.
Speed
In terms of speed, even though encryption might slow down the internet connection, with a good VPN, the user might not even notice it. In fact, by hiding users’ traffic, VPNs can increase the connection speed in case of ISP throttling. Consequently, ISPs cannot inspect the traffic or services used and deliberately restrict users’ internet speed.
On the other hand, the use of a free proxy server can result in a slower connection speed too, because one server cannot withstand large loads if many people use it at the same time.
That said, a proxy caching feature can increase traffic and web page loading speed. For instance, proxy servers can cache web pages or files on the proxy servers themselves to share those resources with one or several users.
Price
While many proxy servers are free, virtual private networks usually come with a price tag. This means that a VPN provider that offers paid services is more likely to invest in higher-quality equipment and users’ privacy.
On the other hand, free proxies and VPNs do not necessarily ensure the maximum security of users’ private data. For example, anyone can use free proxies without investing any money. In this case, these connections can be not only slower but also less secure.
Also, the providers of free services cannot profit from subscriptions as the providers of paid services. Still, they have to make money to support their business. As a result, free proxy and VPN service providers might sell user data for marketing purposes or serve annoying ads.
Similarities
While VPNs and proxies offer different services, they both enhance online anonymity. Both conceal IP addresses and the geographical location by acting as the middlemen between the user and the internet. No matter which service the user chooses, any third party ends up seeing the IP address of a proxy or VPN server.
Both proxies and VPNs offer free and paid options. Needless to say, users should use free services with caution.

Should you use VPN or proxy?
While considering what service you should use, think about what you want to hide. If you just want to hide your IP address, a proxy will do.
If you are an individual internet user and want more anonymity online without investing a lot of money in a pricey VPN, you can configure a free proxy on your device yourself. You can even download a browser extension for easier configuration.
Individuals and smaller companies might benefit from using a proxy server if they need to anonymize browsing for their employees. Also, with the help of proxies, companies may track employees’ search histories, allow them to access geo-restricted websites or block certain websites (e.g., social media sites) to increase productivity.
Ultimately, if you also want to protect the data you transfer or receive, a VPN might be a better choice. If you have a large business, a VPN might be more suitable, thanks to encryption features that help protect the data you send.
If you take online privacy seriously, consider investing in a premium VPN client that offers data encryption, high-quality security and many server locations to choose from. Remember to be more cautious about free VPN services because these are more likely to put your data at risk.
One last thing to note is that neither of these services can offer you complete privacy in today’s digital world.
Conclusion
Both a VPN and proxy server connect users to a remote server and provide a different IP address for anonymous browsing. Yet, VPNs and proxies are different. Basically, it all comes down to reliability and security. While not all proxies can encrypt traffic, premium VPNs offer strong encryption services to ensure a more reliable connection to the internet.
Of course, whether you choose a proxy or VPN service depends on your needs. Some users simply want to hide their IP addresses when browsing without paying a lot of money. Others may be after more substantial protection while shopping or performing online banking transactions.
Although both businesses and individual internet users might want to be invisible on the internet, it’s important to note that neither of the two services can ensure complete anonymity. That said, both VPNs and proxies can help increase online privacy to some extent.
About the author
Table of contents
What is a VPN server?
Types of VPN
What is a proxy server?
Types of proxy server protocols
HTTP
SOCKS
FTP
TLS
Comparing VPN vs. proxy
Security
Proxy security
VPN security
Encryption
Speed
Price
Similarities
Should you use VPN or proxy?
Conclusion
Related reading

DNS and rDNS: the Hidden Heroes That Keep the Internet Running
Discover the web's overlooked helpers - DNS & rDNS. Learn their importance, benefits, and automation's role in powering the online world.
Read more
Email Service Provider: What You Should Know About ESPs in 2022
Discover the differences between email service providers and webmail clients. Learn the importance of ESPs for successful email marketing campaigns.
Read more
File Transfer Protocol Explained
What does FTP stand for? What is the importance of this protocol? How does it work? Read this post to learn all about the File Transfer Protocol.
Read moreSubscribe to the IPXO email and don’t miss any news!
